Data Orchestration 101: Process, Benefits, Challenges, and Tools

Table of Contents
Dashboards go stale, stakeholders slip on decisions, and on-call engineers chase failed jobs at 4 a.m. As data volume and tools multiply, keeping pipelines reliable, compliant, and cost aware gets harder, not easier.
Modern stacks span warehouses, lakes, streams, and dozens of SaaS sources. Teams need a single control plane to plan and run jobs in the right order, manage dependencies and retries, enforce policies, and react to events in real time. That operating model is powered by data orchestration.
In this article you will learn what data orchestration is and how it works, how it differs from ETL, data integration, and basic automation, the core benefits and common pitfalls, practical best practices and an implementation playbook, key security, privacy, and compliance considerations, real world examples you can reuse, and a quick comparison of popular tools to help you choose the right fit.
If you are a data engineer or a CTO, use this article to align teams on process, set clear SLAs, and design pipelines that stay reliable as you scale.
Table of Contents
What is data orchestration?
Data orchestration is the process of gathering siloed data from various locations across the company, organizing it into a consistent, usable format, and activating it for use by data analysis tools. Data orchestration enables businesses to take various fragmented data pipelines and turn them into rich insights that drive more agile decision-making. Automation runs a single task on its own; orchestration coordinates multiple automated tasks into an end-to-end workflow with decisions, retries, and alerts.
What is the orchestration layer?
The orchestration layer refers to a layer of the modern data platform that empowers data teams to more easily manage the flow of data within and across data environments. Instead of manually managing the flow of an ETL pipeline, the orchestration layer employs a specific tool to automate—or “orchestrate”—the flow of data.
Value companies can generate from data orchestration tools
- Faster time-to-insights. Automated data orchestration removes data bottlenecks by eliminating the need for manual data preparation, enabling analysts to both extract and activate data in real-time.
- Improved data governance. By centralizing various disparate data sources, data orchestration tools help companies better understand the scope of their data and improve its governance.
- Enhancing compliance. Data orchestration helps companies comply with various international privacy laws and regulations, many of which require companies to demonstrate the source and rationale for their data collection.
- Positioning the company for scale. As data volume grows, scheduling becomes critical to successfully managing your data ingestion and transformation jobs. Data orchestration enables data teams to easily understand, prepare, and manage pipelines at scale.
How data orchestration works
When you’re extracting and processing data, the order of operation matters. Data pipelines don’t require orchestration to be considered functional—at least not at a foundational level. However, once data platforms scale beyond a certain point, managing jobs will quickly become unwieldy by in-house standards.
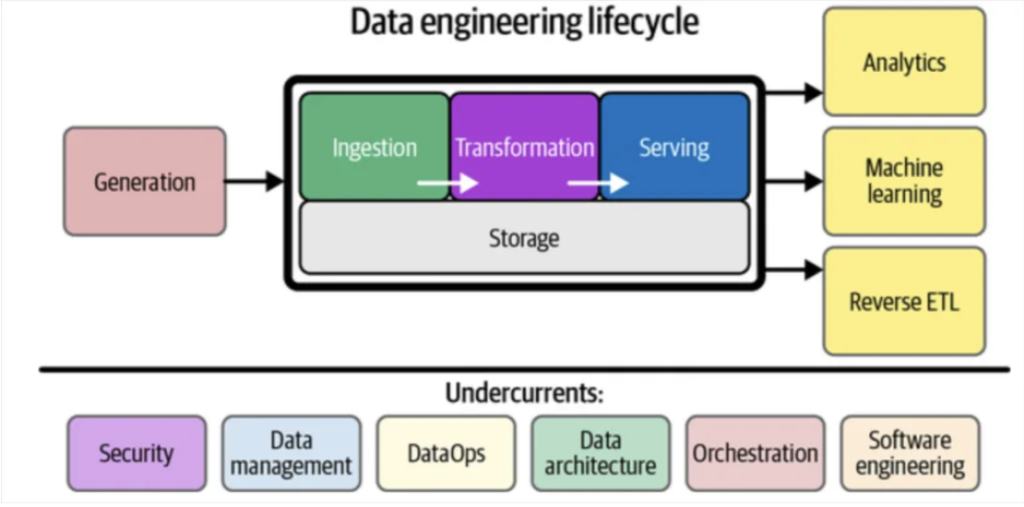
Data orchestration supports the data engineering lifecycle by bringing automation to data pipelines. Source: Fundamentals of Data Engineering by Joe Reis and Matt Housley.
Common orchestration triggers
• Schedule-based (e.g., hourly, daily SLAs)
• Event-based (e.g., file arrival, CDC event, webhook)
• API/manual (human-in-the-loop approvals)
Reliability primitives
• Idempotency for safe retries
• Backoff + circuit breaking for flaky dependencies
• Data contracts to validate schemas before runs
• Lineage + run history to accelerate incident response
Data orchestration brings automation to the process of moving data from source to storage by configuring multiple pipeline tasks into a single end-to-end process.
3 steps of data orchestration
- The organization phase, in which data orchestration tools gather and organize data pipelines.
- The transformation phase, in which various fragmented data is converted to a consistent, accessible, and usable format.
- The activation phase, in which data orchestration tools deliver usable data for transformation and visualization.
While data orchestration tools might not be required for a pipeline to be considered “functional,” they’re nonetheless an essential component of the modern data stack, and serve as the connective tissue among various data warehouses.
A good modern orchestration tool will be cloud-based to support the modern data stack and user-friendly enough to be leveraged by domains like marketing outside the data engineering team.
So, who’s responsible for data integration? While data integration and data pipeline architecture has traditionally been a responsibility of the data engineering team, the popularity of data mesh architectures has led some teams to share this responsibility with domain leaders as well to facilitate federated data ownership. While that’s certainly not a requirement for data teams—and is even pretty hotly debated amongst data leaders—whether or not you ascribe to a mesh architecture will undoubtedly impact what orchestration tooling is right for your team.
5 Benefits of data orchestration tools
Data orchestration tools can yield significant benefits for organizations—from driving efficiency across the data team to improving relationships across business domains. Let’s take a look at a few of those benefits in detail.
1. Automating data workflows
Nowadays, every company is effectively a data company—and with more and more data pipelines to manage, data engineers are spread increasingly thin. Automating data workflows makes data usable more quickly and enables data engineers to focus on more higher-value tasks that drive ROI for the organization.
2. Eliminating data silos
Siloed data can be a real problem. While siloes often develop naturally as organizations scale, resolving data siloes is rarely as straightforward. Migrating to a single location is often unrealistic for most companies, but not addressing siloes can complicate everything from pipeline management to data governance. Data orchestration enables data leaders to remove data silos without depending on manual migration. Centralizing data and making it accessible also supports better data governance and compliance.
3. Faster time to insights for data analysts
A huge value that data orchestration tools provide is time. Data orchestration takes inaccessible and inconsistent data and makes it organized and usable in real-time. This means analysts can easily leverage the most current data without engineering bottlenecks, delivering faster insights for critical business use cases.
4. Unlocking data across business domains
Teams across business domains increasingly rely on data to make informed and mission-critical decisions. While that’s no doubt good news for your data team, data will often find itself in various domain silos as a result. Data orchestration breaks down those barriers, enabling greater visibility for your data team and greater cross-functional analysis for business leaders across the organization.
5. Strengthening compliance and reducing risk
Orchestration centralizes control of where data moves and who can run what, which makes it easier to honor opt-outs and deletion requests and to prove data lineage during audits. Combined with data observability, you can prevent bad or non-compliant data from propagating.
Steps to follow when implementing data orchestration
Use these steps to move from ad hoc jobs to reliable, observable pipelines. Revisit them each quarter so improvements stick and drift stays in check.
1. Inventory pipelines and owners
Start with a complete inventory. List each pipeline and dataset with an owner, SLA or SLO, criticality, schedule, and cost profile. Map upstream and downstream dependencies, note on-call rotation, and flag risky jobs. Turn this into a living catalog that new work must register before it runs.
2. Pick a fit for use orchestrator
Choose a platform that matches how your team builds. Decide between code first or low code, and managed or self hosted. Check support for event triggers, retries, backfills, secrets, access control, and run visibility. Pilot in one domain, write lightweight standards, and only then expand.
3. Model dependencies
Declare how work relates so jobs run in the right order. Use events for freshness sensitive data and schedules where they make sense. Add contracts, timeouts, retries, idempotency, and conditional paths so failures are contained and recovery is predictable. Prefer asset based graphs when you want lineage and ownership to be obvious.
4. Shift left on quality
Validate data at ingestion and before every transform. Check schema, nulls, duplicates, distributions, and referential integrity. Block downstream steps on violations, open incidents with context, and quarantine bad outputs until fixed. Record what failed and why so you can tune thresholds over time.
5. Wire lineage and alerting
Send run status and quality results to the tools your team already uses. Make every alert actionable with dataset, run ID, owner, upstream impact, last good run, and links to logs. Route by severity and service, dedupe related failures, and track freshness and SLA adherence on shared dashboards.
6. Harden security
Apply least privilege and clear roles. Scope secrets per environment, rotate keys, and keep audit logs for who ran what and when. Tag assets by region and sensitivity, and enforce policy as code in CI so changes without owners, tags, or regions fail fast. Test deletion and opt out flows on a schedule.
7. Measure ROI
Publish a small KPI set and review it regularly. Track freshness, SLA hit rate, failed run rate, MTTR, percent of auto retries that succeed, cost per run, and engineering hours saved. Use the trends to retire dead jobs, tune schedules, and focus effort where reliability and savings move together.
Security, privacy, and compliance in data orchestration
Start by building security, privacy, and compliance into how workflows run. Use least privilege so only the right people can trigger, edit, or view pipelines. Handle PII at the edges by masking or tokenizing sensitive fields at extract, and enforce column-level policies during transforms so sensitive data does not leak into the wrong tables.
Once the controls are in place, make your workflows observable and provable. Capture run metadata, inputs, outputs, and lineage so every change is traceable. Orchestrate deletion and opt-out requests end to end so records are removed from every downstream store on time. Treat governance as code by checking policies in CI, enforcing naming and ownership, and blocking changes that do not meet your standards.
Close the loop with routine practice and measurement. Run deletion and DSAR drills on a schedule, verify residency and retention policies in a lower environment before rollout, rotate secrets and keys regularly, and review access by role each quarter. Gate deployments with policy checks so jobs that miss required tags, owners, or regions fail fast, and track simple KPIs like DSAR SLA hit rate, audit log completeness, and time to revoke access so privacy is measured, not assumed.
Best practices to follow for effective data orchestration
As organizations wrestle with ever-growing data volumes, the difference between success and failure often comes down to orchestration strategy. The following practices help teams build data pipelines that deliver reliable insights without constant firefighting.
Prioritize scalability
When a streaming service processes viewing data from hundreds of millions of subscribers worldwide, their data workflows can’t stumble over volume. Designing for scale means building systems that grow gracefully, not ones that require constant rebuilding.
Start with modular workflows. Instead of creating one monolithic pipeline that handles everything from data ingestion to analysis, break processes into discrete, reusable components. A retail company might separate inventory updates, sales processing, and customer analytics into independent workflows that run in parallel rather than sequentially.
Cloud-native tools excel here. Platforms like Apache Airflow or Prefect allow teams to distribute workloads across multiple servers automatically. When holiday traffic spikes, a well-designed system spins up additional resources without manual intervention. The alternative, rigid, server-bound workflows, creates bottlenecks that can bring operations to a standstill during peak times.
Ensure visibility and transparency
Data teams need to see what’s happening inside their pipelines, not just whether they succeeded or failed. The difference resembles knowing your package was delivered versus tracking its journey through every distribution center.
Modern orchestration platforms offer dashboards that display real-time workflow status, processing times, and data lineage. When a music platform’s recommendation engine updates, engineers can trace exactly which data sources fed into each playlist suggestion. This visibility helps teams spot slowdowns before they become failures.
Business stakeholders benefit too. A marketing director doesn’t need to understand the technical details, but seeing that customer segmentation data updates every hour, with clear indicators when something goes wrong, builds trust and enables better decision-making. Simple visualization tools like dependency graphs show how data flows through the organization, making the invisible visible.
Bake in data quality from day one
Treat data quality as part of the workflow, not an afterthought. Define clear data contracts at the edges of your pipelines so expectations are explicit before any job runs.
Validate the basics on every run. Check row counts, nulls, duplicates, distributions, and referential integrity. Block downstream steps when checks fail and surface the why with run context, owners, and lineage so the right team can fix it fast.
Fail fast, recover fast. Open incidents automatically, quarantine bad outputs, and backfill once issues are resolved. Over time, tune thresholds and tests to match how your datasets actually behave.
Design for cost and performance
Plan around assets, not timers. Use event-driven and asset-based orchestration so work only runs when data changes or an upstream signal arrives. This cuts idle compute and reduces noisy schedules.
Make every step efficient. Prefer incremental models, partition large tables, and cache intermediate results where it helps. Right-size resources per task and parallelize only where it shortens wall-clock time without spiking costs.
Set SLAs and SLOs by dataset. Tie freshness targets to business value, track cost-per-run and cost-per-query, and alert when spend drifts from plan. The goal is reliable pipelines that stay fast and affordable as volume grows.
Embrace automation wisely
Automation excels at repetitive tasks but struggles with exceptions. The key lies in knowing where to draw the line.
Automate the predictable. Daily sales reports, regular data quality checks, and scheduled backups all benefit from automation. An e-commerce platform might automate product listing updates for standard inventory while flagging items with unusual pricing patterns or missing specifications for manual review. This approach ensures quality control without slowing down routine operations.
Human oversight remains essential for strategic decisions and anomaly handling. When machine learning models drift from expected performance, automated systems should alert data scientists rather than blindly retraining. Similarly, while automated testing can verify data format and data completeness, only human judgment can determine whether a sudden spike in user registrations represents success or a bot attack.
The most effective orchestration strategies treat automation as a powerful assistant, not a replacement for human expertise.
Real-world data orchestration examples
Real-world data orchestration scenarios demonstrate how organizations coordinate complex workflows across multiple systems and timescales. These examples illustrate the practical challenges that orchestration platforms solve, from managing dependencies to handling failures gracefully.
E-commerce inventory and pricing synchronization
A large online retailer needs to coordinate inventory levels, pricing updates, and product recommendations across multiple systems every night. The orchestration workflow begins at midnight, pulling sales data from the transaction system, updating inventory counts across warehouses, and recalculating dynamic pricing based on demand patterns.
The orchestration platform manages dependencies between these tasks. Inventory updates must complete before the pricing algorithm runs, which must finish before the recommendation engine retrains. If warehouse system updates fail, the orchestrator prevents downstream processes from using stale data. It also triggers alerts to the operations team and attempts automated recovery.
This coordination prevents scenarios where customers see available products that are actually out of stock, or where pricing doesn’t reflect current inventory levels. The orchestration layer provides a complete audit trail, showing exactly when each system updated and how data flowed through the pipeline.
Financial fraud detection and transaction processing
A major bank orchestrates real-time fraud detection across millions of daily transactions, coordinating between payment systems, risk models, and customer notification services. When a credit card transaction occurs, the orchestration system routes it through multiple validation steps within milliseconds, checking spending patterns, geographic anomalies, and merchant reputation scores.
The orchestrator manages both real-time and batch processes. While individual transactions flow through instant fraud checks, the system also runs hourly pattern analysis across all accounts and nightly model retraining based on newly identified fraud cases. These different timescales must coordinate seamlessly, with batch job insights feeding back into real-time decision-making.
Complex decision trees determine the workflow path. Suspicious transactions might trigger additional authentication requests, temporary account holds, or manual review queues, while normal transactions proceed directly to settlement. The orchestration platform ensures each transaction follows the appropriate path while maintaining audit trails for regulatory compliance. If any component fails, the system gracefully degrades, allowing legitimate transactions to continue while queuing suspicious ones for later analysis.
Multi-source content delivery for streaming platforms
A video streaming service orchestrates content from multiple sources including live broadcasts, on-demand libraries, and user-generated uploads. The orchestration system coordinates video transcoding, metadata enrichment, content delivery network distribution, and recommendation engine updates for millions of assets daily.
When new content arrives, the orchestrator triggers parallel workflows. Video files go through quality checks and transcoding into multiple resolutions. Simultaneously, metadata extraction pulls information about genres, actors, and themes. Natural language processing analyzes subtitles and descriptions. All these processes must be completed before the content becomes available to viewers.
The orchestration platform adapts to varying workloads. During major sports events, it scales up live stream processing while maintaining on-demand content pipelines. It prioritizes popular content for faster processing and manages storage costs by orchestrating archival workflows for older, less-viewed material. This complex choreography happens automatically, ensuring viewers always have fresh content available while optimizing infrastructure costs.
Data orchestration vs. data integration
While often confused, data orchestration and data integration serve fundamentally different purposes in modern data architectures. Understanding their distinctions helps organizations choose the right approach for their specific needs.
Data integration focuses on combining data from different sources into a unified view. It’s about moving and transforming data so systems can share information. When a hospital merges patient records from multiple departments into a single database, that’s integration. The goal is creating connections between disparate data sources.
Data orchestration, by contrast, manages the entire workflow of data processes. It coordinates when integration happens, monitors its progress, handles failures, and triggers downstream actions. Orchestration doesn’t move data itself but ensures all the moving parts work together harmoniously. It’s the conductor directing the symphony, not the musicians playing instruments.
Consider a retail chain updating inventory across stores. Integration would handle combining sales data from each location into a central warehouse. Orchestration would schedule these updates, ensure they complete successfully, trigger restocking alerts when inventory runs low, and notify managers if any store’s data fails to sync.
The distinction becomes clearer in practice. Integration answers “how do we connect these systems?” Orchestration answers “how do we manage all these connections efficiently?”
Choose integration when you need to solve specific connectivity problems between systems. A company merging after an acquisition needs integration to unite their customer databases. Choose orchestration when managing complex workflows with multiple dependencies. That same company needs orchestration to coordinate nightly updates across all integrated systems, handle errors gracefully, and ensure data flows smoothly from source to destination.
Many organizations need both. Integration provides the pipes, orchestration ensures water flows through them at the right time, in the right order, to the right places. Success comes from recognizing when each tool fits the task at hand.
Common data orchestration challenges
While data orchestration is certainly helpful in centralizing siloed data and speeding actionability, it’s also not without its challenges. From increasing complexity to introducing new data quality risks, understanding the challenges inherent to pipeline automation will enable your data team to maximize the value of your data orchestration tooling.
Increased orchestration process complexity
Obviously, one of the primary benefits of data orchestration tools is the ability to reduce complexity within an organization’s pipeline operations. But even with the most advanced tooling, pipelines can still become complex. Sometimes just the act of introducing new tooling can add to that complexity. Having a clear understanding of your goals and the needs of your stakeholders will help you respond quickly as complexities arise.
Skills and maintenance overhead
New platforms add a learning curve. Teams juggle upgrades, new patterns, and glue code that grows over time. Without guardrails, every team builds flows a little differently, which makes onboarding slow and handoffs risky.
Keep the platform simple to run and simple to use. Make common tasks repeatable. Reduce one-off work so engineers spend time on data, not framework care and feeding.
Lack of compatibility with disparate data tools
To function effectively, data orchestration tools need to integrate with every data repository in the organization. When that cannot happen, gaps emerge not only in your ability to manage pipelines but also in your ability to fully realize their value. Select managed cloud solutions that integrate with existing, scalable tooling, and proactively manage tech debt to maximize compatibility and capture the greatest value from your data orchestration investment.
Monitoring sprawl
Logs live in one place, metrics in another, and alerts fire in every channel. The same failure shows up as multiple pages with little context. On-call gets noisy, triage is slow, and real issues hide behind alert fatigue.
Bring run history, lineage, and alerts into a single view. Make every alert actionable with clear ownership and next steps. Cut noise so the right person sees the right signal at the right time.
Data quality issues introduced by faster data workflows
Accessible data doesn’t necessarily correlate to reliable data. As data moves more quickly through pipelines and analysts depend on it for more real-time use-cases, the importance of both data integrity and data reliability increases exponentially.
The best time to deal with a data quality incident is before it happens. And those incidents will be coming fast and furious as your pipeline velocity increases. Utilizing an end-to-end data observability tool will provide immediate quality coverage as pipelines grow and provide a platform for deeper quality coverage as SLAs are established for specific pipelines.
Keeping up with regulations and compliance. Data orchestration facilitates data compliance by offering businesses more control and oversight of their data sources. However, as with data quality, when it comes to compliance all that speed can come at a cost. Automation should be established with regulations in mind on the front end to ensure customer data is only being ingested and stored when and how it’s legally permissible to do so.
6 Popular data orchestration tools
If you’re looking to add a data orchestration tool to your data stack, you’re in luck. As the data landscape continues to evolve, new data orchestration tools are evolving with it. For data teams considering their first orchestration tool, there are multiple open-source, cloud-based, and user-friendly options to scratch the itch. There are even a few free solutions if you’re into that sort of thing.
1. Apache Airflow
Apache Airflow has become the industry standard for workflow orchestration, offering a Python-based platform for authoring, scheduling, and monitoring data pipelines. Originally developed at Airbnb, it treats workflows as code, allowing teams to version control their pipeline definitions. The platform’s maturity and widespread adoption mean extensive documentation and community support. Its directed acyclic graph (DAG) structure provides clear visualization of task dependencies and execution flow.
Benefits
Airflow’s code-first approach appeals to engineering teams who prefer defining workflows programmatically. Its extensive library of pre-built operators connects to virtually any data source or service. The web interface provides clear visualization of pipeline dependencies and execution history. Active community support ensures continuous improvements and troubleshooting resources.
Use cases
Airflow excels at batch processing workflows where teams need complex dependency management. Data warehouses rely on it for ETL pipelines that run on fixed schedules. Machine learning teams use it to orchestrate model training pipelines with multiple preparation steps. Companies with existing Python infrastructure find it integrates seamlessly into their technology stack.
2. Metaflow
Metaflow , developed by Netflix and now open source, focuses specifically on data science workflows, making it easier for scientists to build and deploy production-ready models. The framework handles infrastructure complexity automatically, letting data scientists focus on their algorithms rather than engineering concerns. It provides built-in versioning, experiment tracking, and seamless scaling from laptops to cloud compute. Metaflow bridges the gap between prototyping and production by maintaining the same code across both environments.
Benefits
Data scientists can develop locally and deploy to production without code changes. Built-in versioning tracks every run, parameter, and artifact automatically. The framework handles compute scaling transparently, from local execution to thousands of cloud instances. Integration with popular data science libraries feels natural to Python developers.
Use cases
Machine learning teams use Metaflow to manage end-to-end model development pipelines. Research teams appreciate its ability to track experiments and reproduce results reliably. Organizations building recommendation systems benefit from its proven scalability. Data scientists transitioning models from notebooks to production find its gradual learning curve appealing.
3. Stitch Data Orchestration
Stitch is a a low-code platform for building and managing data pipelines, emphasizing visual development over programming. The platform offers pre-built connectors to hundreds of data sources and destinations, reducing integration complexity. Its cloud-native architecture handles infrastructure management automatically, letting teams focus on data flow logic. Stitch targets organizations that need reliable data movement without maintaining engineering teams.
Benefits
Visual pipeline builders enable non-technical users to create sophisticated data workflows. Pre-built connectors eliminate custom integration development for common systems. Automatic schema migration handles source system changes without manual intervention. Cloud-based execution removes infrastructure management overhead entirely.
Use cases
Marketing teams use Stitch to consolidate data from multiple advertising platforms. Small businesses without dedicated data engineers rely on it for basic ETL needs. Analytics teams appreciate quick setup times for new data source connections. Organizations consolidating SaaS application data find its connector library particularly valuable.
4. Prefect
Prefect calls itself “air traffic control for your data.” This solution leverages a modern alternative to traditional orchestrators, emphasizing simplicity and developer experience while maintaining enterprise capabilities. The platform addresses common pain points in workflow management through smart defaults and minimal configuration. Its hybrid architecture lets teams run workflows anywhere while maintaining centralized monitoring. Prefect’s design philosophy prioritizes making simple things easy and complex things possible.
Benefits
Prefect eliminates much of Airflow’s configuration complexity through smart defaults and intuitive APIs. Its hybrid execution model allows teams to run data workflows anywhere while maintaining central visibility. Dynamic workflow generation enables data-driven pipeline creation. The platform handles retries and error recovery automatically, reducing operational overhead.
Use cases
Startups and mid-size companies choose Prefect for its quick setup and minimal maintenance requirements. Data science teams appreciate its native support for parameterized workflows and experiment tracking. Organizations migrating from cron jobs find Prefect’s gentle learning curve appealing. Real-time data processing scenarios benefit from its event-driven capabilities.
5. Dagster
Dagster reimagines orchestration around data assets rather than tasks, providing a framework that understands what data exists and how it’s transformed. This asset-centric approach makes dependencies explicit and enables better testing and development practices. The platform treats data quality as a first-class concern, building validation directly into pipeline definitions. Its software-defined assets concept brings software engineering best practices to data pipeline development.
Benefits
Asset-based orchestration makes data lineage visible and testable by default. Built-in data quality checks catch issues before they propagate downstream. The development environment mirrors production closely, reducing deployment surprises. Type checking and data validation happen automatically throughout pipeline execution.
Use cases
Analytics engineering teams use Dagster to manage dbt models alongside other data transformations. Financial institutions appreciate its emphasis on data correctness and auditability. Companies building data products benefit from treating datasets as first-class citizens. Organizations focused on data governance find its built-in cataloging features valuable.
6. Astronomer Data Orchestration
Astronomer provides a managed platform for Apache Airflow, eliminating the operational complexity of running orchestration infrastructure. The company offers both cloud-hosted and on-premises deployment options with enterprise-grade security and support. Its platform enhances vanilla Airflow with improved monitoring, easier deployment processes, and operational tools. Astronomer focuses on making Airflow production-ready without requiring deep infrastructure expertise.
Benefits
Managed infrastructure reduces the operational burden of maintaining Airflow clusters. Enhanced monitoring and alerting catch issues before they impact production workflows. One-click deployments simplify the process of promoting code through environments. Enterprise features like role-based access control and audit logs satisfy compliance requirements.
Use cases
Enterprises choosing Airflow but lacking infrastructure expertise rely on Astronomer’s managed service. Organizations with strict security requirements use its on-premises deployment options. Teams scaling beyond single-server Airflow installations benefit from built-in cluster management. Companies needing commercial support for their orchestration infrastructure find Astronomer’s expertise valuable.
Trends shaping data orchestration
Data teams are rethinking how they coordinate work as stacks expand and real time becomes the default. The trends below show where orchestration is heading and what to build into your roadmap over the next 12 months.
Real time and streaming
More workloads now expect data within minutes, not days. Fraud detection, IoT telemetry, and in-app personalization all rely on streams that trigger work as events arrive. Orchestration needs to handle event signals, incremental materializations, and late or out-of-order data without breaking downstream consumers. Start with event driven triggers, make tasks idempotent, set freshness targets in minutes, and add backoff and replay so you can recover without manual work.
Hybrid and multi cloud
Data lives across regions and providers for latency, residency, and vendor risk. Orchestration should route work where the data sits, respect data classes, and fail over cleanly when a zone or provider is unavailable. Tag assets with region, provider, and sensitivity, keep secrets and connections scoped to those tags, and design dependencies that avoid costly cross-cloud hops unless required.
Asset based orchestration
Teams are moving from step centric DAGs to assets as first class citizens. You declare datasets, their dependencies, and freshness expectations, then run only what changed. This reduces waste and makes data lineage and ownership clearer for every table or feature set. Define assets with owners, SLOs, and checks, recompute on upstream change or failed validation, and track versions so you can roll forward or back with confidence.
AI assisted operations
Machine learning can group noisy alerts, summarize incidents, suggest likely root causes, and propose runbook steps. Some remediations can be automated safely, like rerunning a task after a transient failure or increasing a timeout within a guardrail. Start with triage and summarization, keep humans in the loop for changes that affect data semantics, and measure impact with MTTR, failed-run rate, and the share of incidents resolved without paging.
Data contracts at the edges
Producers and consumers agree on schema and semantics before data moves. Data contracts are versioned, validated at ingestion, and enforced in orchestration so breaking changes fail fast and do not leak downstream. Store contracts in git, require owners and deprecation windows for any change, block runs on contract violations, and notify subscribers with lineage so migrations are planned, not surprises.
How to ensure data trust across ETL orchestrated pipelines
Orchestration makes data move; data observability makes sure the data and the runs are right. Treat data quality checks, lineage-aware alerting, and run-level SLOs as first-class steps in every workflow. If freshness is hourly, alert on upstream delays before SLAs are missed, and auto-quarantine suspect tables until checks pass.
There’s no doubt that orchestrating data delivers faster speed to insights; but it’s not just the data that will be moving faster through your pipelines. As pipeline velocity increases, the speed of data quality issues will too.
When data quality issues arise, end-to-end data observability gives data teams at-a-glance visibility into the upstream and downstream dependencies affected by orchestration. And as your data orchestration grows, automated data quality checks ensure that your quality coverage grows right along with it.
Orchestration turns scattered jobs into reliable, auditable workflows. Pair it with data observability and clear SLAs, and you’ll ship fresher insights with fewer firefights, even as volume and velocity climb.
Ready to drive even more value from your orchestration tooling? Learn how Monte Carlo can scale data reliably across your entire pipeline and ensure high-quality data at the orchestration level and beyond.
Our promise: we will show you the product.






